函数式接口

函数式接口
| name | type | description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 消费型接口 | Consumer | Consumer< T > | 接收T对象,不返回值 |
| 断定型接口 | Predicate | Predicate< T > | 接收T对象并返回boolean |
| 函数型接口 | Function | Function< T, R > | 接收T对象,返回R对象 |
| 供给型接口 | Supplier | Supplier< T > | 提供T对象(例如工厂),不接收值 |
Consumer
接收T对象,不返回值, 只有入参,没有返回值。
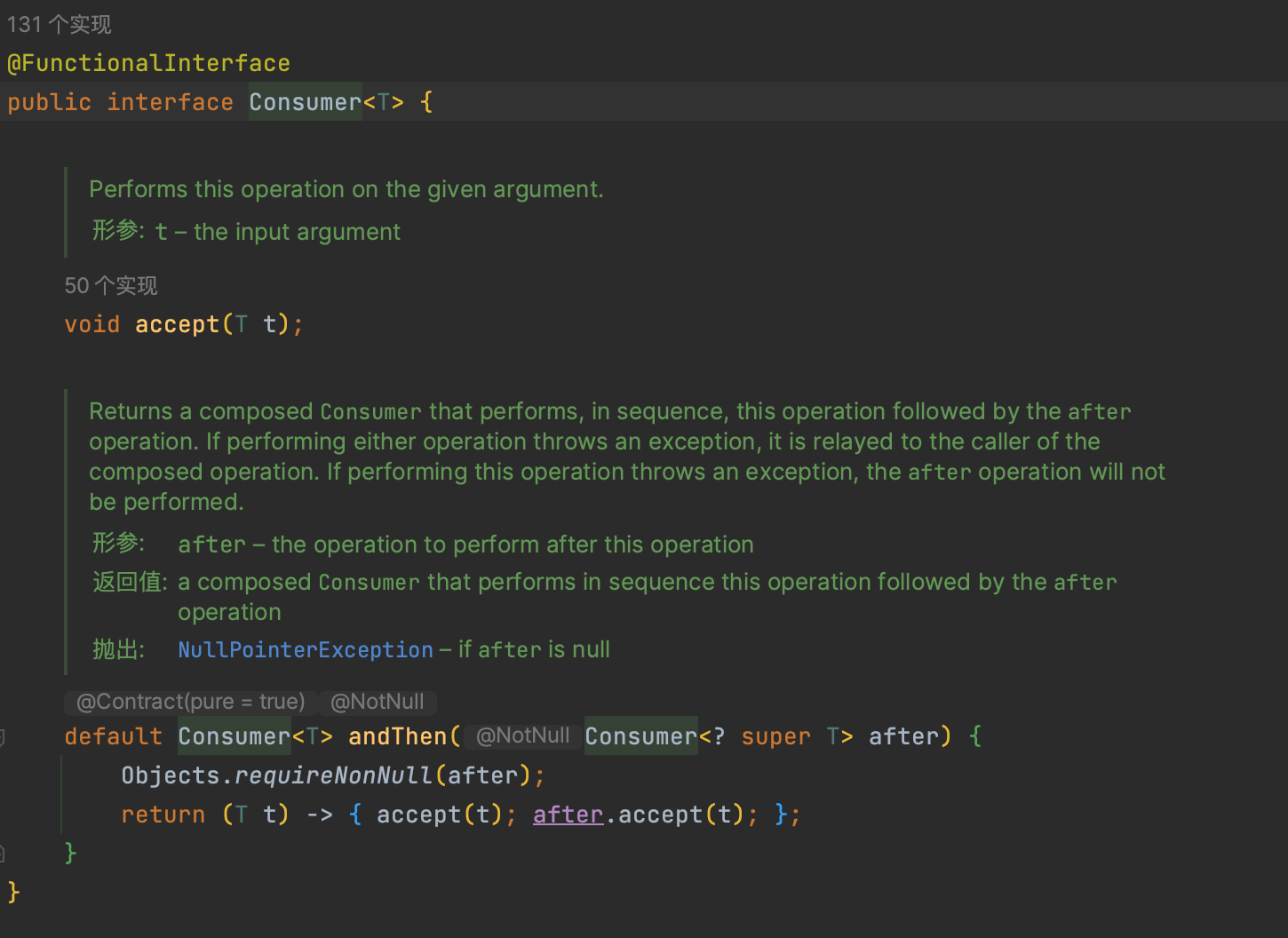
实现一个循环打印
public class Java8ConsumerForEach {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 消费函数定义
Consumer<String> printConsumer = System.out::println;
// 使用
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("java", "node", "http://wuc0714.top/");
forEach(list, printConsumer);
}
public static <T> void forEach(List<T> list, Consumer<T> consumer) {
for (T t : list) {
consumer.accept(t);
}
}
}
有一个健身房,大家都去健身房锻炼,但是每个人锻炼的内容不一样
package com.example.demo;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
// 有一个健身房,大家都去健身房锻炼,但是每个人锻炼的内容不一样
public class TheGymConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TheGym bill = new TheGym("小李", "练腿");
theGym(bill, s -> System.out.println(s.getName() + s.getContent()));
TheGym xiaoWang = new TheGym("小王", "慢跑");
theGym(xiaoWang, s -> System.out.println(s.getName() + s.getContent() + "看美女"));
TheGym xiaoSun = new TheGym("小孙", "慢跑");
theGym(xiaoSun, s -> {
//如果小王也在练慢跑,那么小孙就去举重
if (xiaoWang.getContent().equals(s.getContent())) {
s.setContent("举重");
}
System.out.println(s.getName() + s.getContent());
});
// 小孙今天体力好,两组训练一起上
theGym(xiaoSun
, s -> {
System.out.println("第一组训练:" + s.getName() + s.getContent());
}
, s -> {
System.out.println("第二组训练:" + s.getName() + s.getContent());
});
}
/**
* @param t t
* @param consumer 消费者
* @description 健身房
* @author yz
* @date 2022/10/22
**/
public static <T> void theGym(T t, Consumer<T> consumer) {
consumer.accept(t);
}
/**
* @param t t
* @param consumer1 消费者
* @param consumer2 消费者
* @description 健身房
* @author yz
* @date 2022/10/23
**/
public static <T> void theGym(T t, Consumer<T> consumer1, Consumer<T> consumer2) {
consumer1.andThen(consumer2).accept(t);
}
}
输出:
小李练腿
小王慢跑看美女
小孙举重
第一组训练:小孙举重
第二组训练:小孙举重
Predicate
接收T对象并返回boolean
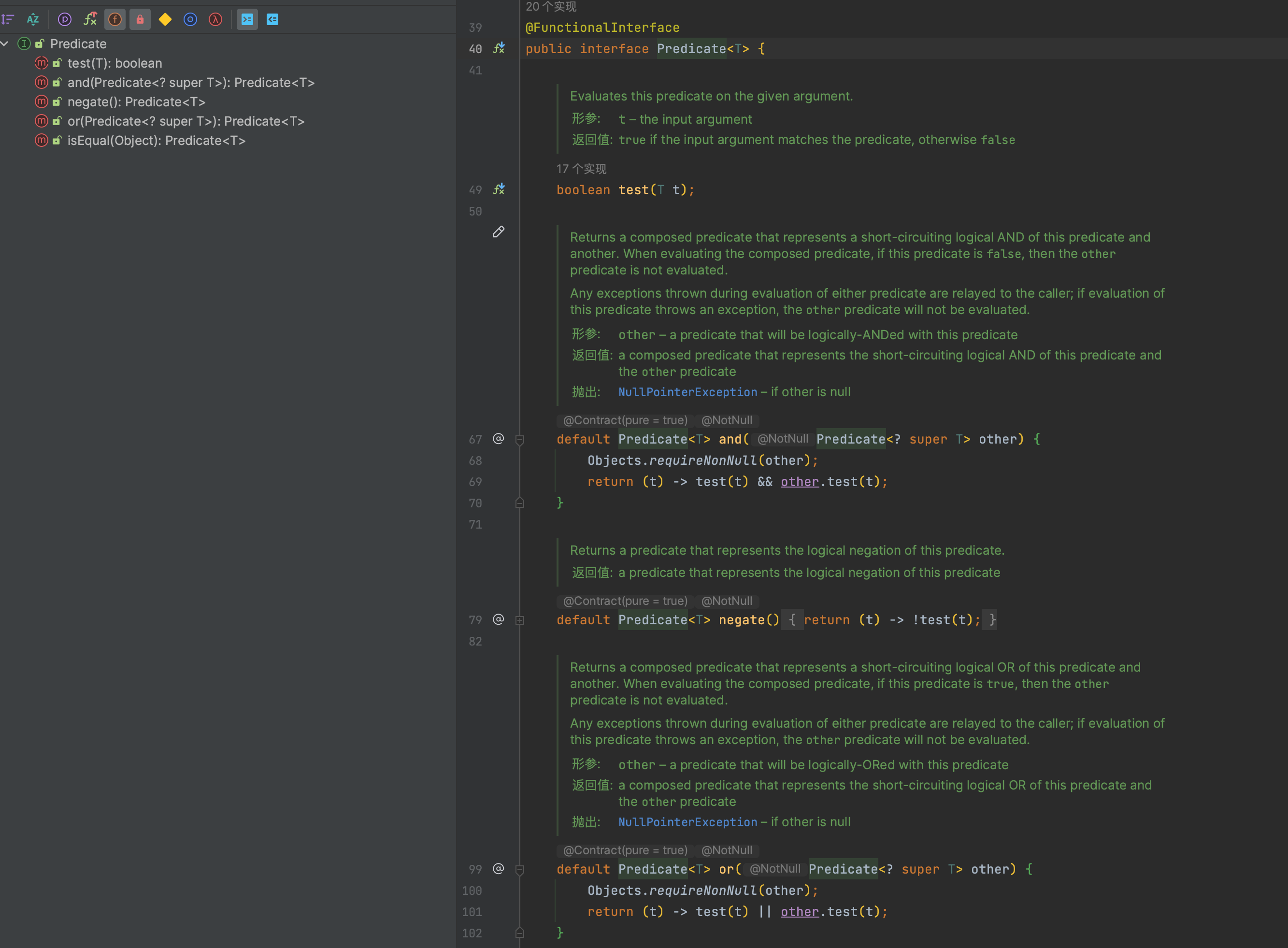
- test
Predicate 函数接口可以用于判断一个参数是否符合某个条件。
@Test
void test() {
Predicate<String> isEmpty = String::isEmpty;
System.out.println(isEmpty.test(""));
System.out.println(isEmpty.test("http://wuc0714.top/"));
}
输出结果:
true
false
- and
使用 and() 方法,可以让前后两个 Predicate 判断条件一起生效。
@Test
void and(){
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Predicate<Integer> greaterThan5 = number -> number > 5;
Predicate<Integer> lessThan9 = number -> number < 9;
Predicate<Integer> filter = greaterThan5.and(lessThan9);
numberList = numberList.stream().filter(filter).collect(Collectors.toList());
//相当于
numberList = numberList.stream().filter(x -> x > 5 && x < 9).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(numberList);
}
输出结果:
[6, 7, 8]
- negate
predicate.negate() 方法会返回一个与指定判断相反的 Predicate。
@Test
void negate() {
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Predicate<Integer> greaterThan5 = number -> number > 5;
numberList = numberList.stream().filter(greaterThan5.negate()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(numberList);
}
输出结果:
[3, 4, 5]
- or
使用 or() 方法,可以让前后两个 Predicate 只需要任意一个条件成立。
@Test
void or() {
List<Integer> numberList = Arrays.asList(3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Predicate<Integer> greaterThan5 = number -> number > 5;
Predicate<Integer> lessThan9 = number -> number < 9;
Predicate<Integer> filter = greaterThan5.or(lessThan9);
numberList = numberList.stream().filter(filter).collect(Collectors.toList());
//相当于
numberList = numberList.stream().filter(x -> x > 5 || x < 9).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(numberList);
}
输出结果:
[3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
- 具体使用
现在我们用一个案例来表示这个怎么使用
@Test
void theGym() {
TheGym bill = new TheGym("小李", "练腿");
// 今日规则 练腿才能入会
Predicate<TheGym> practiceLeg = t -> t.getContent().equals("练腿");
Boolean rule = rule(bill, practiceLeg);
rule = rule(bill, t -> t.getContent().equals("练腿"));
System.out.println("今日规则 练腿才能入会" + rule);
// 今日规则 不练腿才能入会
rule = rule(bill, practiceLeg.negate());
System.out.println("今日规则 不练腿才能入会" + rule);
// 今日规则 练腿和姓名叫小王才能入会
Predicate<TheGym> xiaoWang = t -> t.getName().equals("小王");
rule = rule(bill, practiceLeg.and(xiaoWang));
System.out.println("今日规则 练腿和姓名叫小王才能入会" + rule);
}
/**
* @param t t
* @param predicate 谓词
* @return {@link Boolean }
* @description 规则
* @author yz
* @date 2022/10/23
**/
public static <T> Boolean rule(T t, Predicate<T> predicate) {
return predicate.test(t);
}
输出结果:
今日规则 练腿才能入会true
今日规则 不练腿才能入会false
今日规则 练腿和姓名叫小王才能入会false
Supplier
Supplier没有入参,有返回值.所以多用于对象创建,类似于一个对象创建工厂。可以使用 Lambda 方式创建任意对象,也可以使用对象构造方法的方法引用创对象。
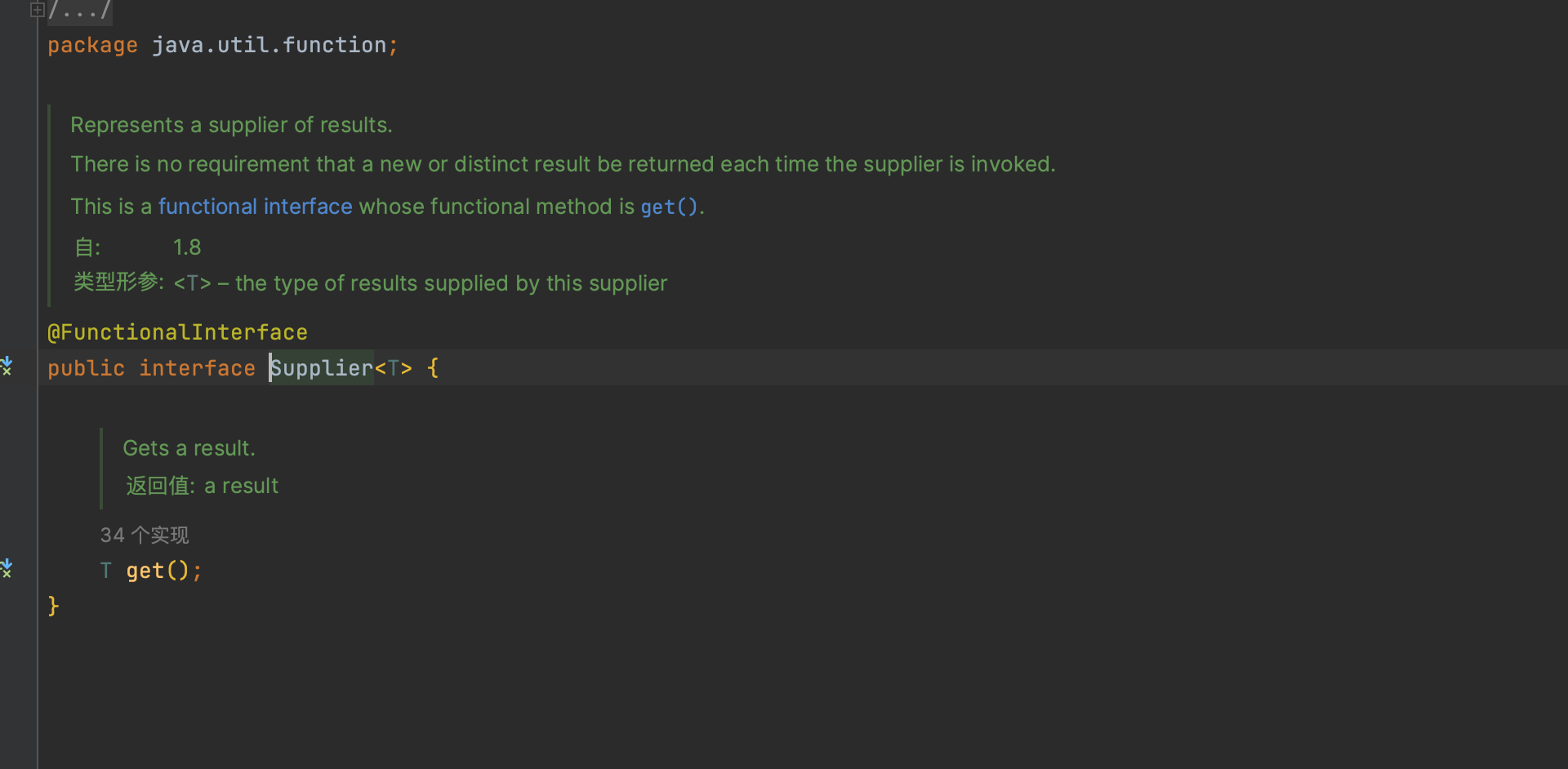
示例 1:使用 Supplier 获取一个 1 到 10 的随机数,使用 Supplier 获取当前时间
@Test
void sample() {
Supplier<Integer> supplier = () -> new Random().nextInt(10);
System.out.println(supplier.get());
System.out.println(supplier.get());
Supplier<LocalDateTime> supplier2 = LocalDateTime::now;
System.out.println(supplier2.get());
System.out.println(supplier2.get());
}
输出结果:
9
0
2022-10-23T02:56:01.238
2022-10-23T02:56:01.238
示例:利用 Supplier 构造一个工厂模式,创建不同类别的健身房。
@Test
void factory() {
TheGym theGym1 = theGymFactory(() -> new TheGym("小李"));
TheGym theGym2 = theGymFactory(() -> new TheGym("小王"));
System.out.println(theGym1);
System.out.println(theGym2);
}
public static TheGym theGymFactory(Supplier<? extends TheGym> supplier) {
TheGym theGym = supplier.get();
theGym.setContent("练腿");
return theGym;
}
输出结果:
TheGym(name=小李, content=练腿)
TheGym(name=小王, content=练腿)
在 Java 8 中,为了方便 Supplier 的使用,提供了指定类型的 Supplier,有 BooleanSupplier, DoubleSupplier, IntSupplier, LongSupplier。
具体使用
健身房每天搞活动,随机抽取一名学员指导健身
@Test
void theGym() {
// 今天抽取一个学员
Supplier<TheGym> xiaoli = () -> new TheGym("小李", "练腰");
exercise(xiaoli);
// 明天抽取一个学员
exercise(() -> new TheGym("小王", "长跑"));
}
/**
* @param supplier 供应商
* @description 锻炼
* @author yz
* @date 2022/10/23
**/
public static void exercise(Supplier<? extends TheGym> supplier) {
TheGym theGym = supplier.get();
System.out.println("今天指导" + theGym.getName() + theGym.getContent());
}
输出结果:
今天指导小李练腰
今天指导小王长跑
Function
接受一个指定对象,返回另外一个指定对象
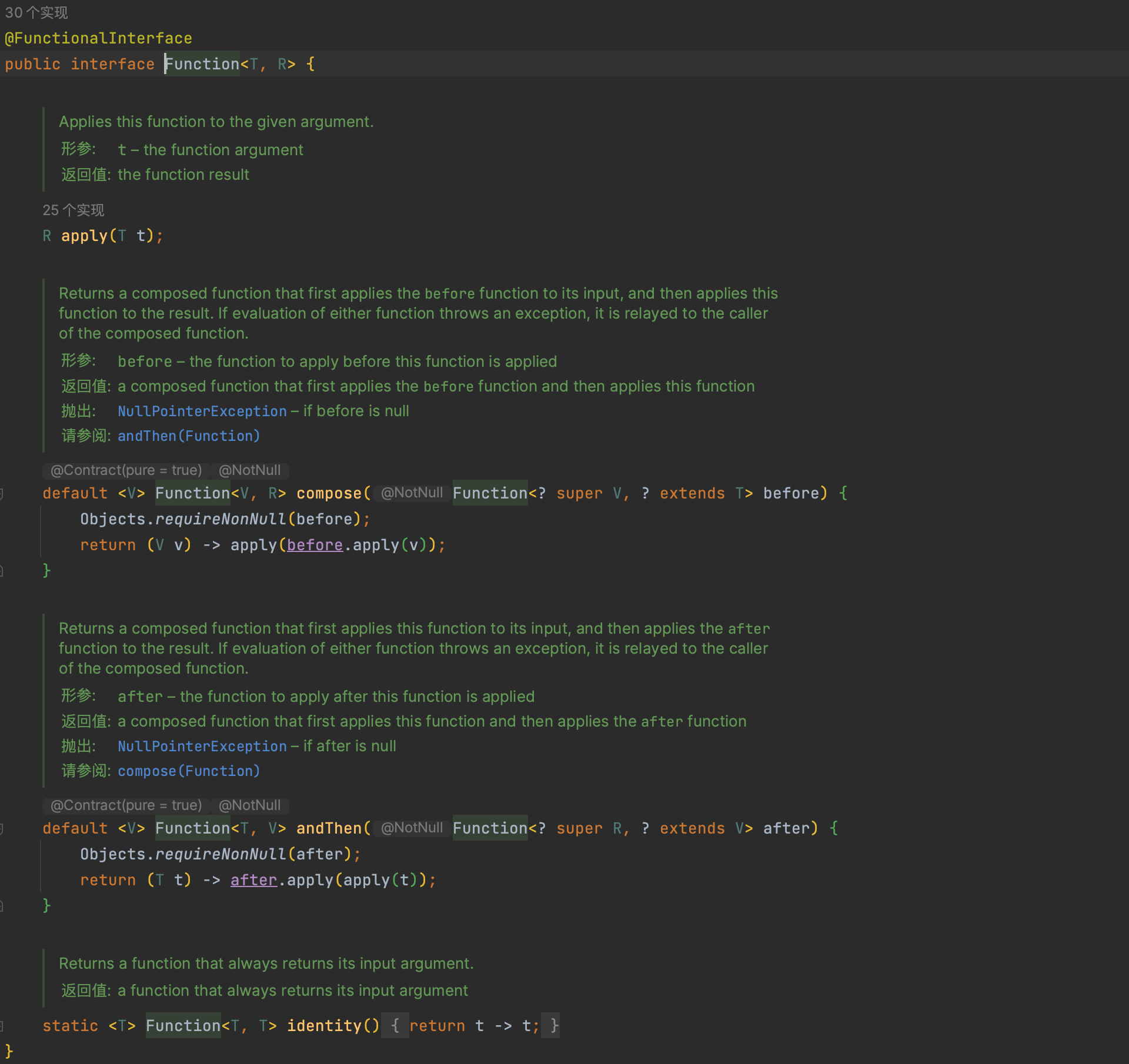
- apply
执行给定的操作
@Test
void apply() {
Function<String, String> toUpperCase = str -> str.toUpperCase();
String result = toUpperCase.apply("http://wuc0714.top/");
System.out.println(result);
}
- compose
源码
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
compose() 方法可以让多个 Function 函数连接使用。通过源码可以分析是参数的apply的先执行
@Test
void compose() {
// 操作1
Function<String, String> toUpperCase = str -> str.toUpperCase();
// 操作2
Function<String, String> increase = str -> str + "post/about/";
// 先执行操作2,再执行操作1
String result = toUpperCase.compose(increase).apply("http://wuc0714.top/");
System.out.println(result);
}
输出结果:
HTTP://WUC0714.TOP/POST/ABOUT/
- andThen
源码
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
andThen() 方法可以让多个 Function 函数连接使用。通过源码可以分析是本体的apply的先执行
@Test
void andThen() {
// 操作1
Function<String, String> toUpperCase = str -> str.toUpperCase();
// 操作2
Function<String, String> increase = str -> str + "post/about/";
// 先执行操作1,再执行操作2
String result = toUpperCase.andThen(increase).apply("http://wuc0714.top/");
System.out.println(result);
}
输出结果:
HTTP://WUC0714.TOP/post/about/
在 vavr中,为了方便 Function 的使用,提供了指定类型的 Function,还有更多参数的 Function1,Function2,Function3,Function4,Function5,Function6,Function7,Function8。
具体使用