Sentienl限流

官方文档:https://sentinelguard.io/zh-cn/docs
使用手册:https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki
一.sentinel引入
1.安装sentinel客户端
2.pom文件导入包
3.配置文件修改
spring:
sentinel:
transport:
#指定控制台
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8858
二.流控规则
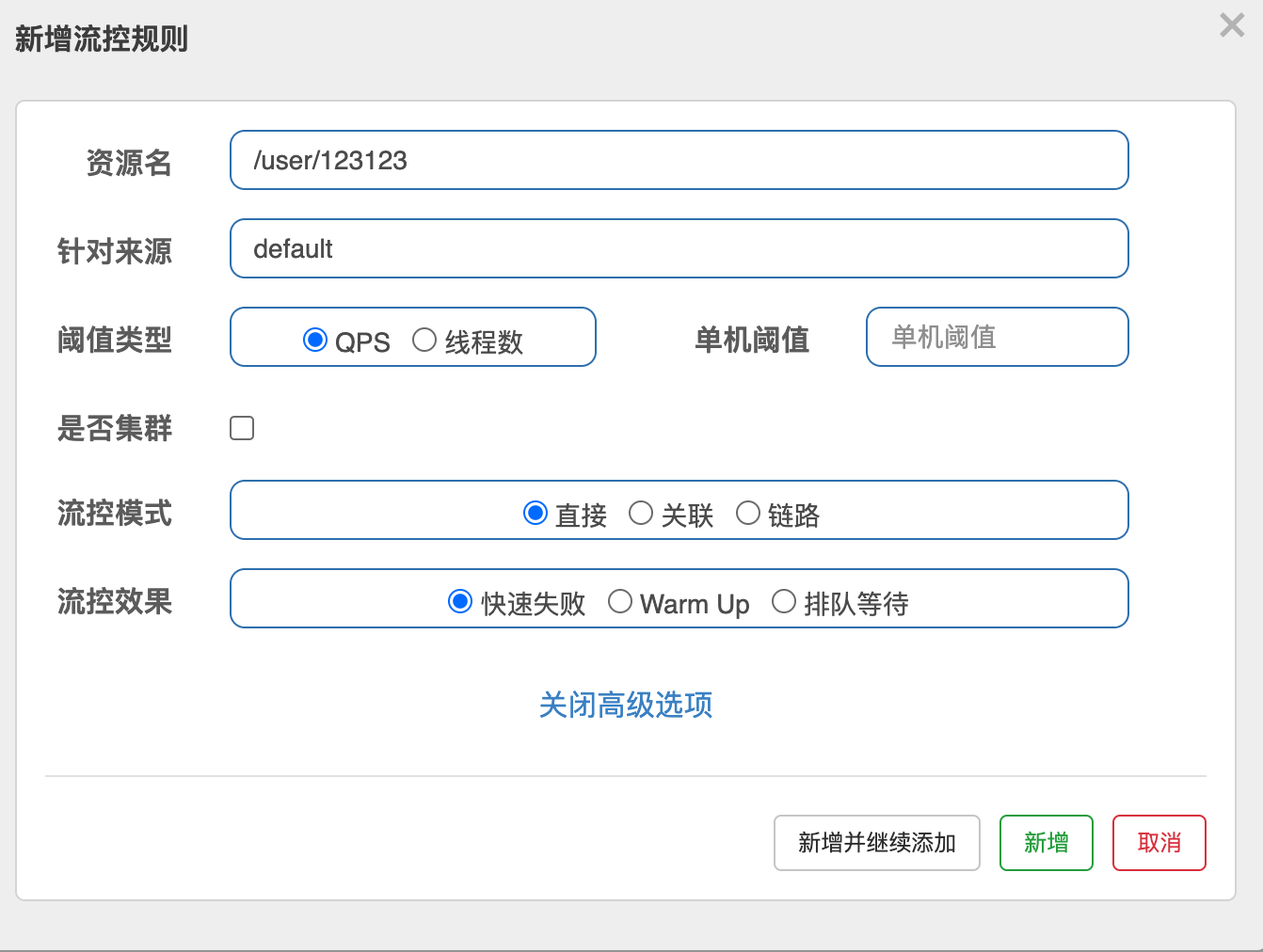
-
资源名: 访问路径
-
针对来源:默认default,填写微服务名,指定对哪个微服务进行限流
-
阈值类型:
- 每秒钟的请求数量,当调用接口的QPS达到阈值的时候,进行限流;
- 当调用接口的线程数达到阈值的时候,进行限流;
- 是否集群:不需要集群
- 流控模式:
- 直接:接口达到限流条件时,直接限流;
- 关联:当关联的资源达到阈值时,就限流自己;
- 链路:只记录指定链路上的流量 (指定资源从入口资源进来的流量,如果达到阈值,就进行限流)【api级别的针对来源】;
- 流控效果:
- 快速失败:直接失败,抛异常;
- Warm Up:根据codeFactor(冷加载因子,默认为3)的值,即请求 QPS 从阈值 / codeFactor,经过预热时长,逐渐升至设定的QPS阈值;
- 排队等待:匀速排队,让请求以匀速的速度通过,阈值类型必须设置为QPS,否则无效;
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| resource | 资源名,资源名是限流规则的作用对象 | |
| count | 限流阈值 | |
| grade | 限流阈值类型,QPS 模式(1)或并发线程数模式(0) | QPS 模式 |
| limitApp | 流控针对的调用来源 | default,代表不区分调用来源 |
| strategy | 调用关系限流策略:直接、链路、关联 | 根据资源本身(直接) |
| controlBehavior | 流控效果(直接拒绝/WarmUp/匀速+排队等待),不支持按调用关系限流 | 直接拒绝 |
| clusterMode | 是否集群限流 | 否 |
代码配置
private void initFlowQpsRule() {
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
// 资源名
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule(resourceName);
// set limit qps to 20 限流阈值
rule.setCount(20);
// 限流阙值类型
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
// 流控针对的调用来源
rule.setLimitApp("default");
// 添加规则
rules.add(rule);
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
三.降级规则
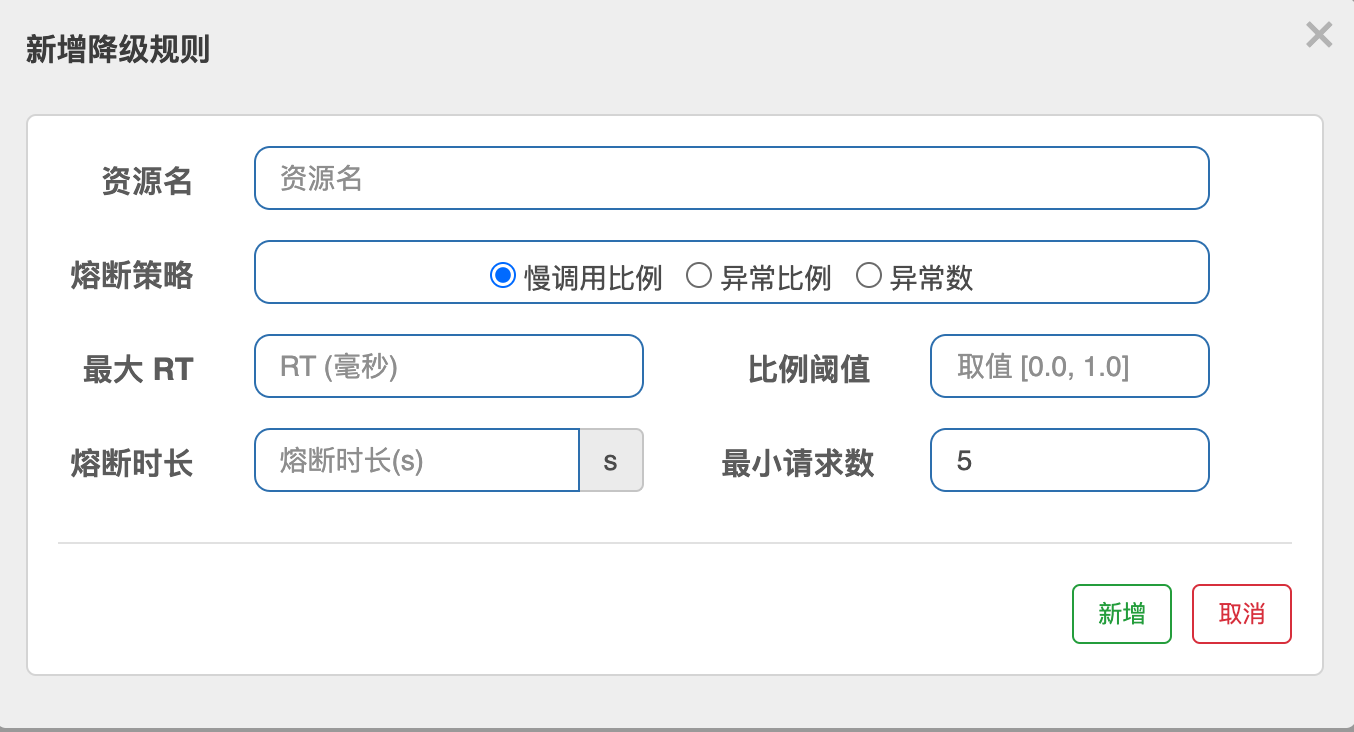
熔断有三种状态,分别为OPEN、HALF_OPEN、CLOSED。
| 状态 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| OPEN | 表示熔断开启,拒绝所有请求 |
| HALF_OPEN | 探测恢复状态,如果接下来的一个请求顺利通过则结束熔断,否则继续熔断 |
| CLOSED | 表示熔断关闭,请求顺利通过 |
1.慢调用比例
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 最大RT | 需要设置的阈值,超过该值则为慢应用 |
| 比例阈值 | 慢调用占所有的调用的比率,范围:[0~1] |
| 熔断时长 | 在这段时间内发生熔断、拒绝所有请求 |
| 最小请求数 | 即允许通过的最小请求数,在该数量内不发生熔断 |
执行逻辑
熔断(OPEN):请求数大于最小请求数并且慢调用的比率大于比例阈值则发生熔断,熔断时长为用户自定义设置。当资源的响应时间超过最大RT(以ms为单位,最大RT即最大响应时间)之后,资源进入准降级状态
探测(HALFOPEN):当熔断过了定义的熔断时长,状态由熔断(OPEN)变为探测(HALFOPEN)。
- 如果接下来的一个请求小于最大RT,说明慢调用已经恢复,结束熔断,状态由探测(HALF_OPEN)变更为关闭(CLOSED)
- 如果接下来的一个请求大于最大RT,说明慢调用未恢复,继续熔断,熔断时长保持一致
2.异常比例
通过计算异常比例与设置阈值对比的一种策略。
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 异常比例阈值 | 异常比例=发生异常的请求数÷请求总数取值范围:[0~1] |
| 熔断时长 | 在这段时间内发生熔断、拒绝所有请求 |
| 最小请求数 | 即允许通过的最小请求数,在该数量内不发生熔断 |
执行逻辑
熔断(OPEN):当请求数大于最小请求并且异常比例大于设置的阈值时触发熔断,熔断时长由用户设置。
探测(HALFOPEN):当超过熔断时长时,由熔断(OPEN)转为探测(HALFOPEN)
- 如果接下来的一个请求未发生错误,说明应用恢复,结束熔断,状态由探测(HALF_OPEN)变更为关闭(CLOSED)
- 如果接下来的一个请求继续发生错误,说明应用未恢复,继续熔断,熔断时长保持一致
3.异常数
通过计算发生异常的请求数与设置阈值对比的一种策略。
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 异常数 | 请求发生异常的数量 |
| 熔断时长 | 在这段时间内发生熔断、拒绝所有请求 |
| 最小请求数 | 即允许通过的最小请求数,在该数量内不发生熔断 |
执行逻辑
熔断(OPEN):当请求数大于最小请求并且异常数量大于设置的阈值时触发熔断,熔断时长由用户设置。探测(HALFOPEN):当超过熔断时长时,由熔断(OPEN)转为探测(HALFOPEN)
- 如果接下来的一个请求未发生错误,说明应用恢复,结束熔断,状态由探测(HALF_OPEN)变更为关闭(CLOSED)
- 如果接下来的一个请求继续发生错误,说明应用未恢复,继续熔断,熔断时长保持一致
由于异常数是一分钟统计一次,所以建议熔断时长设置>60s
三、规则参数说明
熔断降级规则包含下面几个重要的属性:
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| resource | 资源名,即规则的作用对象 | |
| grade | 熔断策略,支持慢调用比例/异常比例/异常数策略 | 慢调用比例 |
| count | 慢调用比例模式下为慢调用临界 RT(超出该值计为慢调用);异常比例/异常数模式下为对应的阈值 | |
| timeWindow | 熔断时长,单位为 s | |
| minRequestAmount | 熔断触发的最小请求数,请求数小于该值时即使异常比率超出阈值也不会熔断(1.7.0 引入) | 5 |
| statIntervalMs | 统计时长(单位为 ms),如 60*1000 代表分钟级(1.8.0 引入) | 1000 ms |
| slowRatioThreshold | 慢调用比例阈值,仅慢调用比例模式有效(1.8.0 引入) |
同一个资源可以同时有多个降级规则。
理解上面规则的定义之后,我们可以通过调用 DegradeRuleManager.loadRules() 方法来用硬编码的方式定义流量控制规则。
private void initDegradeRule() {
List<DegradeRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule();
rule.setResource(KEY);
// set threshold RT, 10 ms
rule.setCount(10);
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_RT);
rule.setTimeWindow(10);
rules.add(rule);
DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
四.热点规则
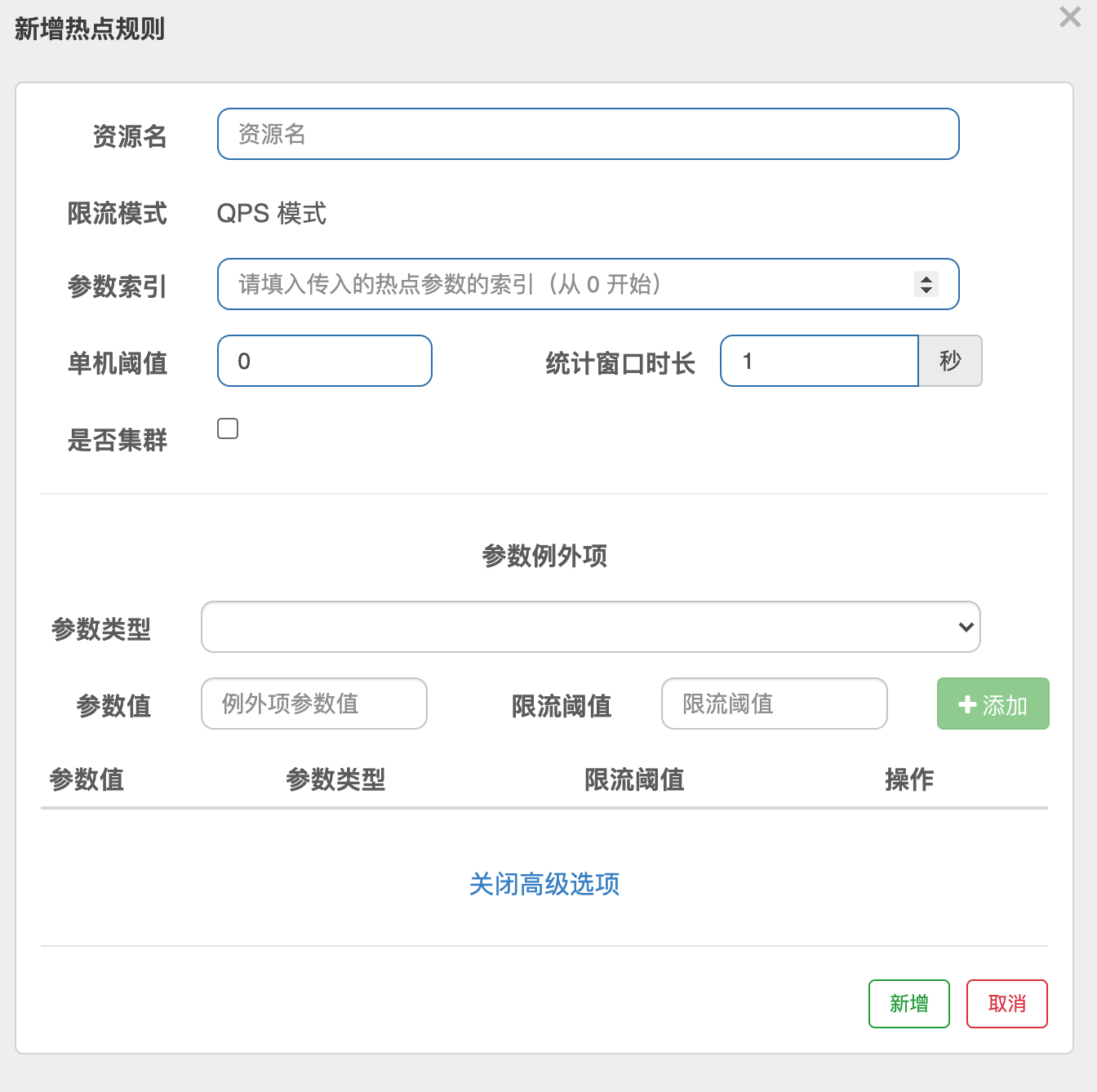
何为热点?热点即经常访问的数据. 比较特殊的流控规则.主要针对参数
| 属性 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| 资源名 | 必填 | |
| 限流模式 | QPS 模式 | |
| 参数索引 | 热点,必填,对应 api 中的参数索引位置 |
|
| 单机阈值 | ||
| 统计窗口时长 | 1s | |
| 是否集群 | false | |
| 高级参数 | ||
| 参数类型 | 可选 | |
| 参数值 | 对应值 | |
| 限流阈值 |
现在我们可以写代码测试一下
@GetMapping("/hot")
@SentinelResource("hot")
public String hot(@RequestParam(required = false) String a, @RequestParam(required = false)String b){
return "a="+a+"b="+b;
}
然后添加热点规则,规则添加到hot上
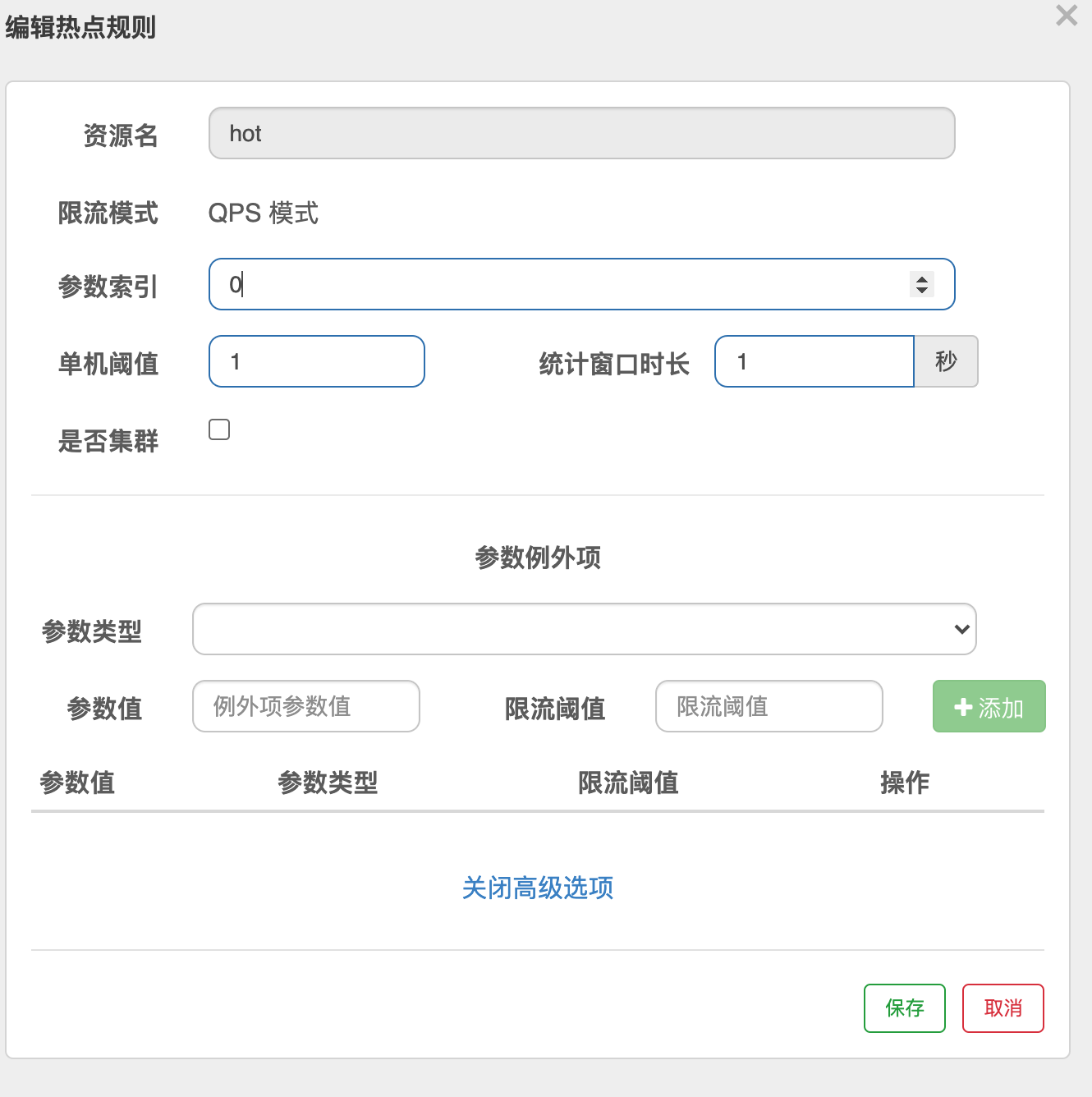
因为索引选择的是0,所有调用 http://127.0.0.1:6020/hot?a=11&b==2,重复调用会限流.但是调用http://127.0.0.1:6020/hot?b==2不会限流
然后添加高级参数
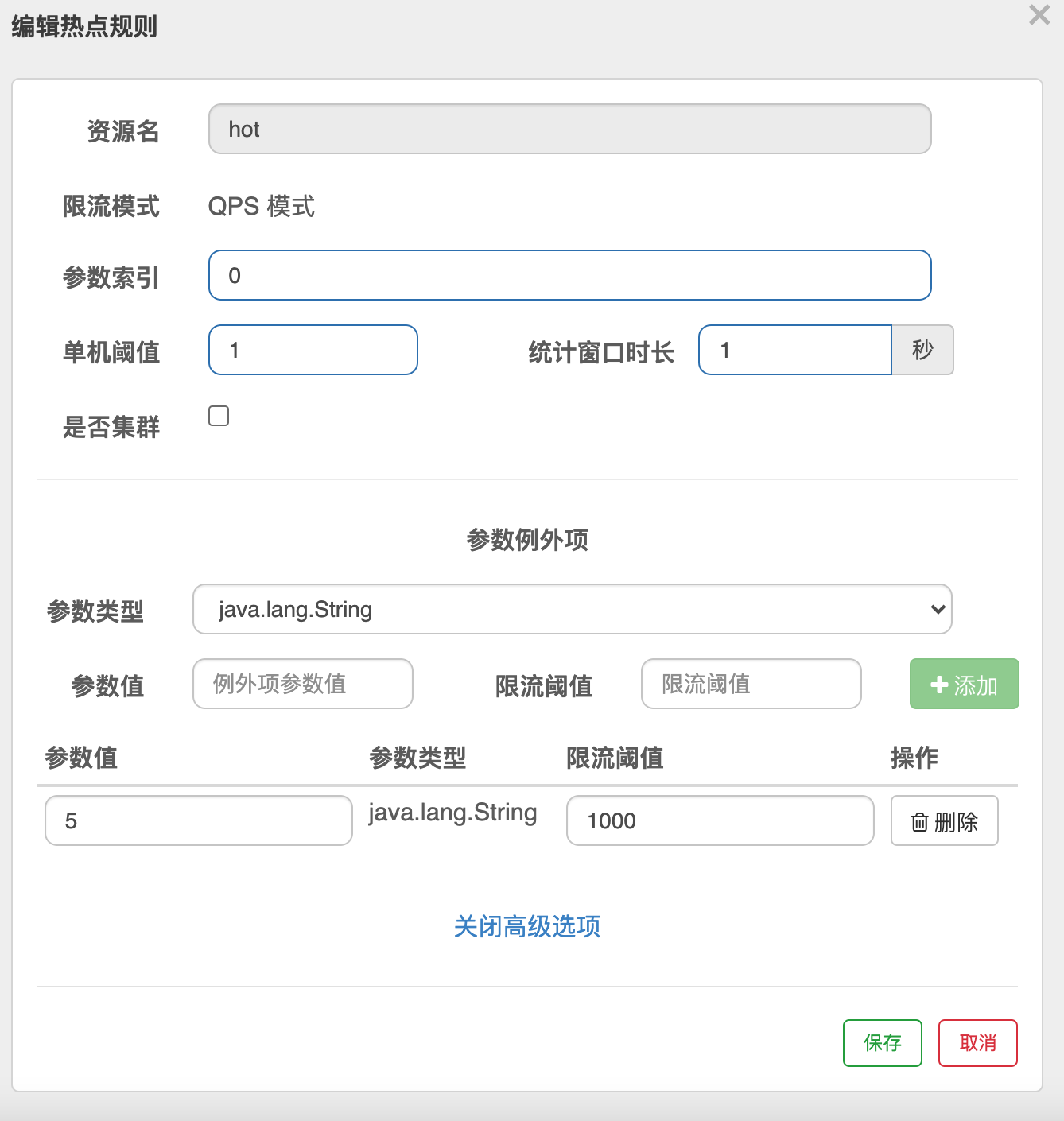
再访问http://127.0.0.1:6020/hot?a=5&b=1他的参数是5,所以匹配上例外参数,他的阈值是1000,正常刷新不会触发限流,但是如果改成http://127.0.0.1:6020/hot?a=1&b=1或者http://127.0.0.1:6020/hot?a=1&b=5他的阈值还是1,会触发限流
五.系统规则 (SystemRule)
Sentinel 系统自适应保护从整体维度对应用入口流量进行控制,结合应用的 Load、总体平均 RT、入口 QPS 和线程数等几个维度的监控指标,让系统的入口流量和系统的负载达到一个平衡,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统整体的稳定性。
Sentinel 系统自适应限流从整体维度对应用入口流量进行控制,结合应用的 Load、CPU 使用率、总体平均 RT、入口 QPS 和并发线程数等几个维度的监控指标,通过自适应的流控策略,让系统的入口流量和系统的负载达到一个平衡,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统整体的稳定性。
系统规则包含下面几个重要的属性:
| Field | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
| highestSystemLoad | load1 触发值,用于触发自适应控制阶段 |
-1 (不生效) |
| avgRt | 所有入口流量的平均响应时间 | -1 (不生效) |
| maxThread | 入口流量的最大并发数 | -1 (不生效) |
| qps | 所有入口资源的 QPS | -1 (不生效) |
| highestCpuUsage | 当前系统的 CPU 使用率(0.0-1.0) | -1 (不生效) |
理解上面规则的定义之后,我们可以通过调用 SystemRuleManager.loadRules() 方法来用硬编码的方式定义流量控制规则。
private void initSystemRule() {
List<SystemRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
SystemRule rule = new SystemRule();
rule.setHighestSystemLoad(10);
rules.add(rule);
SystemRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
}
六.授权规则
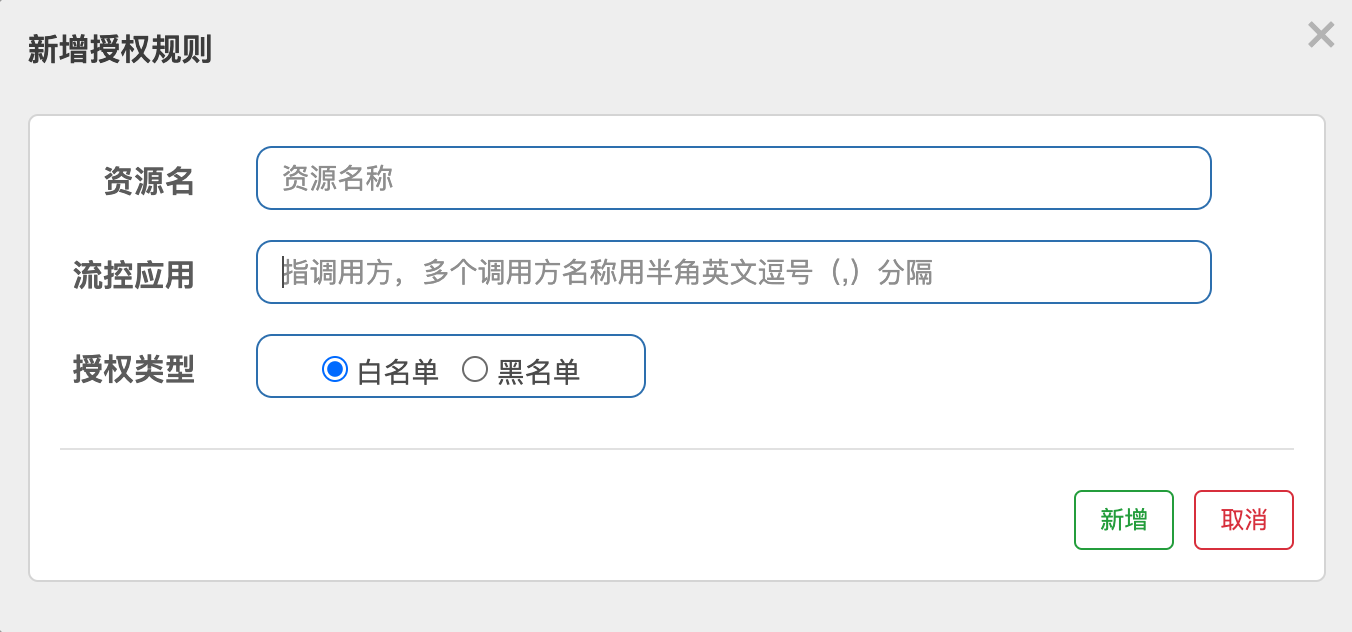
| 属性名字 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 资源名 | 访问地址URL |
| 流控应用 | 调用方,服务名 |
| 授权类型 | 白名单可以调用,黑名单无法调用 |
private void AuthorityRule() {
AuthorityRule rule = new AuthorityRule();
rule.setResource("test");
rule.setStrategy(RuleConstant.AUTHORITY_WHITE);
rule.setLimitApp("appA,appB");
AuthorityRuleManager.loadRules(Collections.singletonList(rule));
}
七.Sentinel与控制台通行原理
Sentinel Dashboard 定时心跳调用注册到控制台上的客户端的API
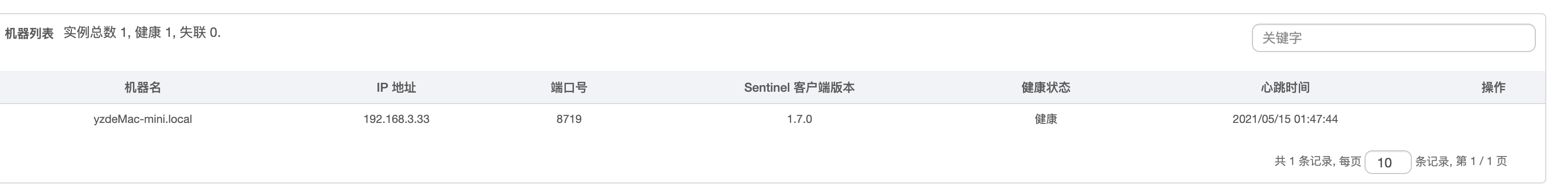
输入http://127.0.0.1:8719/api 查看客户端API
输入 http://127.0.0.1:6020/actuator/sentinel 可以看到客户端定义的端口,心跳,和IP
{
"blockPage": null,
"appName": "spring-cloud-alibaba-feign",
"consoleServer": "127.0.0.1:8858",
"coldFactor": "3",
"rules": {
"systemRules": [],
"authorityRule": [],
"paramFlowRule": [],
"flowRules": [],
"degradeRules": []
},
"metricsFileCharset": "UTF-8",
"filter": {
"order": -2147483648,
"urlPatterns": [
"/*"
],
"enabled": true
},
"totalMetricsFileCount": 6,
"datasource": {},
"clientIp": "192.168.3.33",
"clientPort": "8719",
"logUsePid": false,
"metricsFileSize": 52428800,
"logDir": "/Users/yz/logs/csp/",
"heartbeatIntervalMs": 10000
}
八.控制台相关配置
sentinel:
transport:
#指定控制台
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8858
#指定与控制台通信的IP
#如不配置,会选择一个IP注册
client-ip: 127.0.0.1
# 指定与控制台通信的端口
#默认是8719
port: 8719
# 心跳周期,默认null
#但是在SimpleHttpHeartbeatSender会用默认值10S
heartbeat-interval-ms: 10000
九.@SentinelResource注解使用
@GetMapping("/test-sentinel-api")
@SentinelResource(value = "test-sentinel-api", blockHandler = "block",blockHandlerClass = BlockHandlerClass.class,fallback = "fallback",fallbackClass = FallbackClass.class)
public String testSentinelApi(@RequestParam(required = false) String a) {
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(a)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("参数异常");
}
return a;
}
@Slf4j
public class BlockHandlerClass {
/**
* 处理限流或者降级
* @param a
* @param e
* @return
*/
public String block(String a, BlockException e) {
log.warn("限流");
return "限流";
}
}
@Slf4j
public class FallbackClass {
/**
* 降级
* @param a
* @return
*/
public String fallback(String a,Exception e) {
log.warn("降级");
return "降级";
}
}
十.RestTemplate整合Sentinel
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringCloudAlibabaNacosApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudAlibabaNacosApplication.class);
}
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
@SentinelRestTemplate
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
用户关闭或者启动Sentinel
resttemplate:
sentinel:
enabled: false
十一.feign限流
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: false
十二.sentinel规则持久化
-
1.原始模式
-
2.推模式
-
3.拉模式
| 推送模式 | 说明 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原始模式 | API 将规则推送至客户端并直接更新到内存中,扩展写数据源(WritableDataSource) |
简单,无任何依赖 | 不保证一致性;规则保存在内存中,重启即消失。严重不建议用于生产环境 |
| Pull 模式 | 扩展写数据源(WritableDataSource), 客户端主动向某个规则管理中心定期轮询拉取规则,这个规则中心可以是 RDBMS、文件 等 |
简单,无任何依赖;规则持久化 | 不保证一致性;实时性不保证,拉取过于频繁也可能会有性能问题。 |
| Push 模式 | 扩展读数据源(ReadableDataSource),规则中心统一推送,客户端通过注册监听器的方式时刻监听变化,比如使用 Nacos、Zookeeper 等配置中心。这种方式有更好的实时性和一致性保证。生产环境下一般采用 push 模式的数据源。 |
规则持久化;一致性;快速 | 引入第三方依赖 |
1.原始模式
这种做法的好处是简单,无依赖;坏处是应用重启规则就会消失,仅用于简单测试,不能用于生产环境。
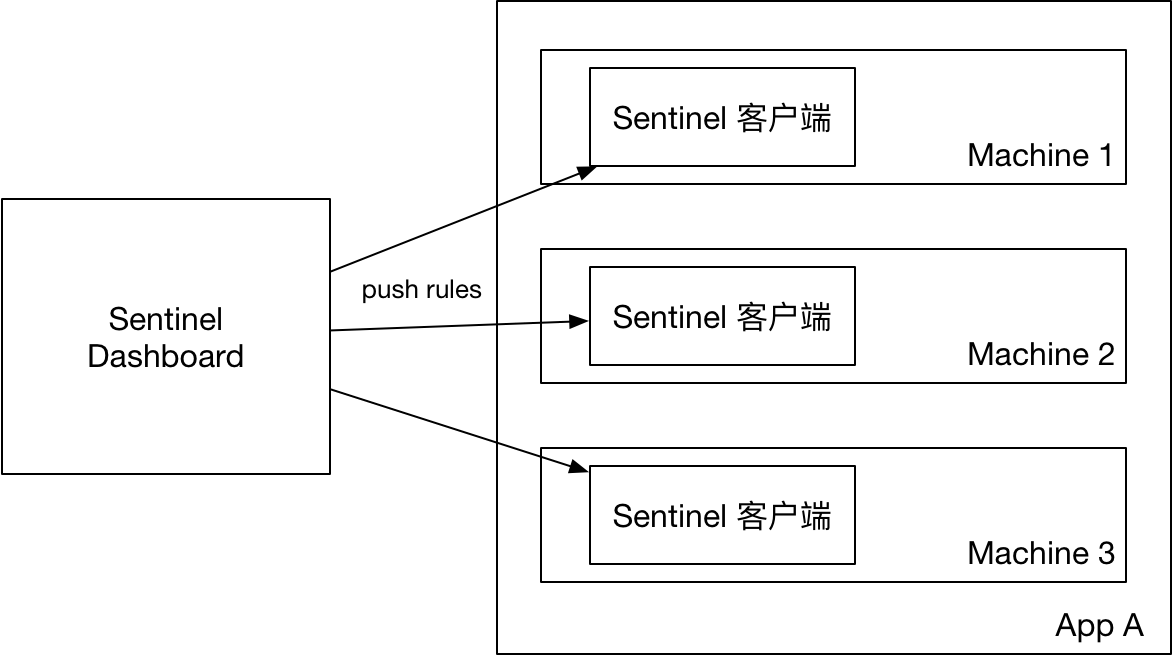
2.推模式
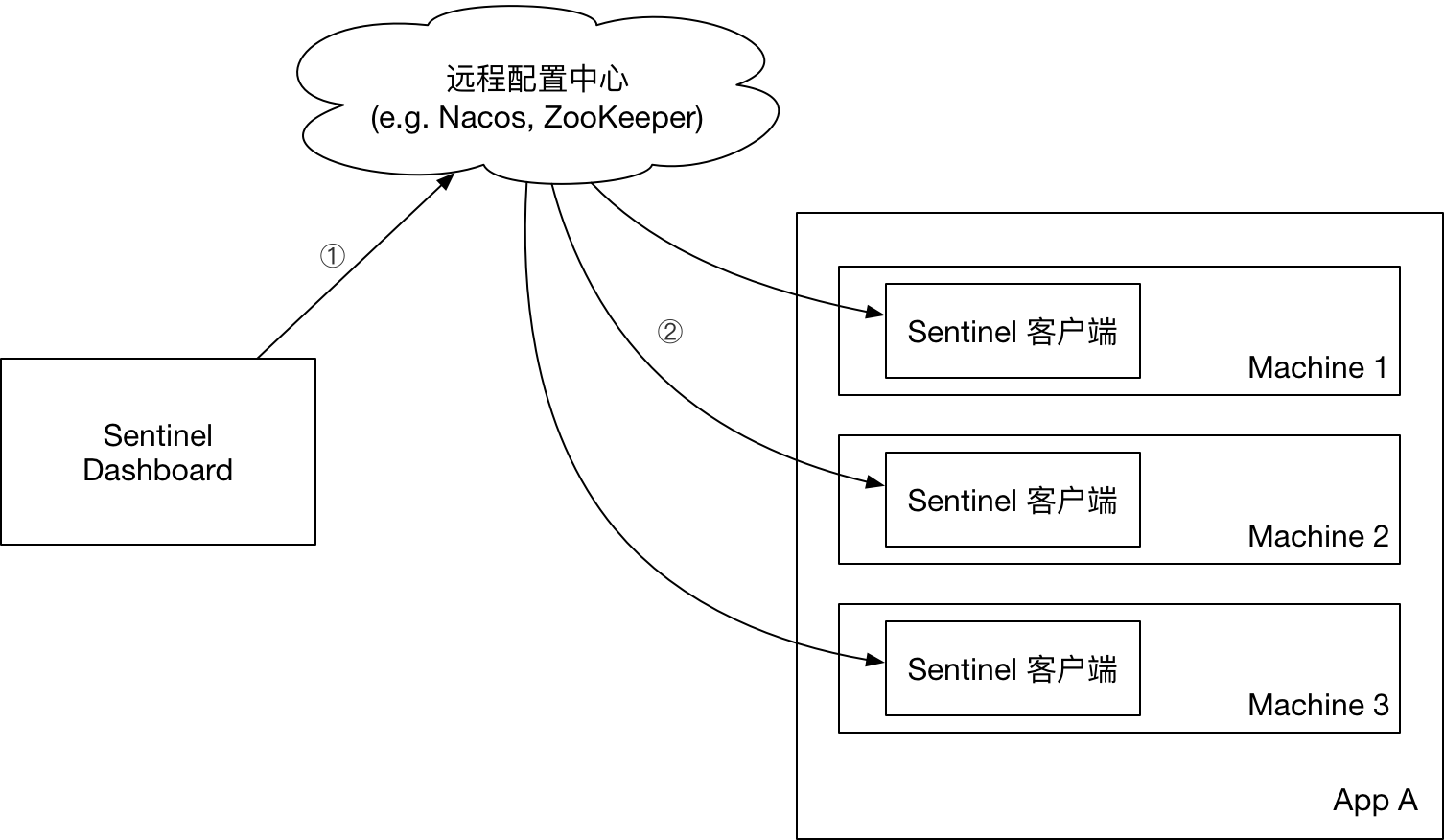
- 控制台推送规则:
- 将规则推送到Nacos或其他远程配置中心
- Sentinel客户端链接Nacos,获取规则配置;并监听Nacos配置变化,如发生变化,就更新本地缓存(从而让本地缓存总是和Nacos一致)
- 控制台监听Nacos配置变化,如发生变化就更新本地缓存(从而让控制台本地缓存总是和Nacos一致)
3.拉模式
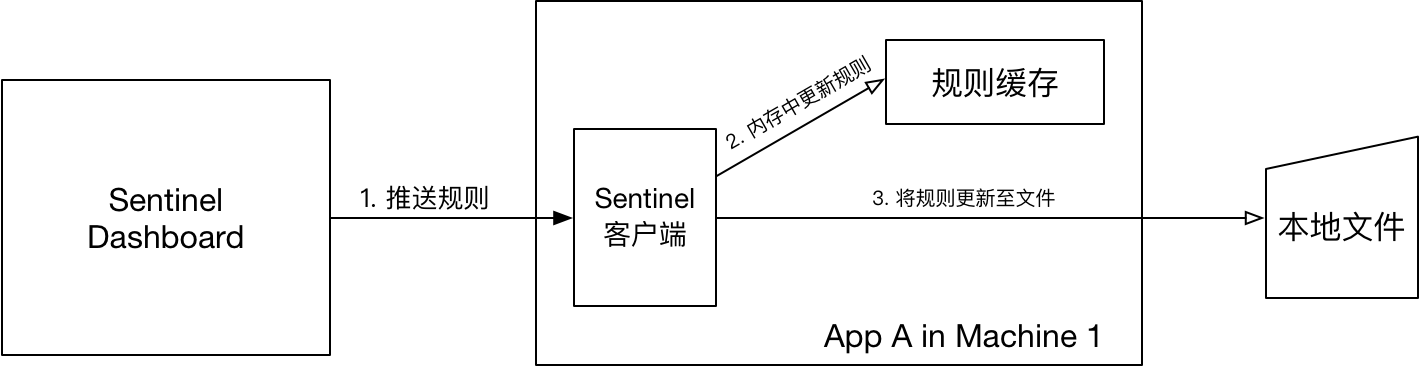
-
FileRefreshableDataSource 定时从指定文件中读取规则JSON文件【图中的本地文件】,如果发现文件发生变化,就更新规则缓存。
-
FileWritableDataSource 接收控制台规则推送,并根据配置,修改规则JSON文件【图中的本地文件】。
代码实现
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.command.handler.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.datasource.*;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.authority.AuthorityRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.FlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.param.ParamFlowRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRule;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.system.SystemRuleManager;
import com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.transport.util.WritableDataSourceRegistry;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 拉模式规则持久化
*
* @author itmuch.com
*/
public class FileDataSourceInit implements InitFunc {
@Override
public void init() throws Exception {
// TIPS: 如果你对这个路径不喜欢,可修改为你喜欢的路径
String ruleDir = System.getProperty("user.home") + "/sentinel/rules";
String flowRulePath = ruleDir + "/flow-rule.json";
String degradeRulePath = ruleDir + "/degrade-rule.json";
String systemRulePath = ruleDir + "/system-rule.json";
String authorityRulePath = ruleDir + "/authority-rule.json";
String paramFlowRulePath = ruleDir + "/param-flow-rule.json";
this.mkdirIfNotExits(ruleDir);
this.createFileIfNotExits(flowRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(degradeRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(systemRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(authorityRulePath);
this.createFileIfNotExits(paramFlowRulePath);
// 流控规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
flowRuleListParser
);
// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager
// 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
flowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
// 将可写数据源注册至transport模块的WritableDataSourceRegistry中
// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);
// 降级规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
degradeRuleListParser
);
DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
degradeRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);
// 系统规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
systemRuleListParser
);
SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
systemRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);
// 授权规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
authorityRuleListParser
);
AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authorityRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
authorityRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authorityRuleWDS);
// 热点参数规则
ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
paramFlowRuleListParser
);
ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());
WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(
paramFlowRulePath,
this::encodeJson
);
ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);
}
private Converter<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<DegradeRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<SystemRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authorityRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<AuthorityRule>>() {
}
);
private Converter<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleListParser = source -> JSON.parseObject(
source,
new TypeReference<List<ParamFlowRule>>() {
}
);
private void mkdirIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
}
private void createFileIfNotExits(String filePath) throws IOException {
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.createNewFile();
}
}
private <T> String encodeJson(T t) {
return JSON.toJSONString(t);
}
}
然后在resources目录下下面添加 MATE-INF>services目录添加 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.init.InitFunc 文件
然后在文件里面添加 所在地址全称例如 com.yz.alibaba.init.FileDataSourceInit